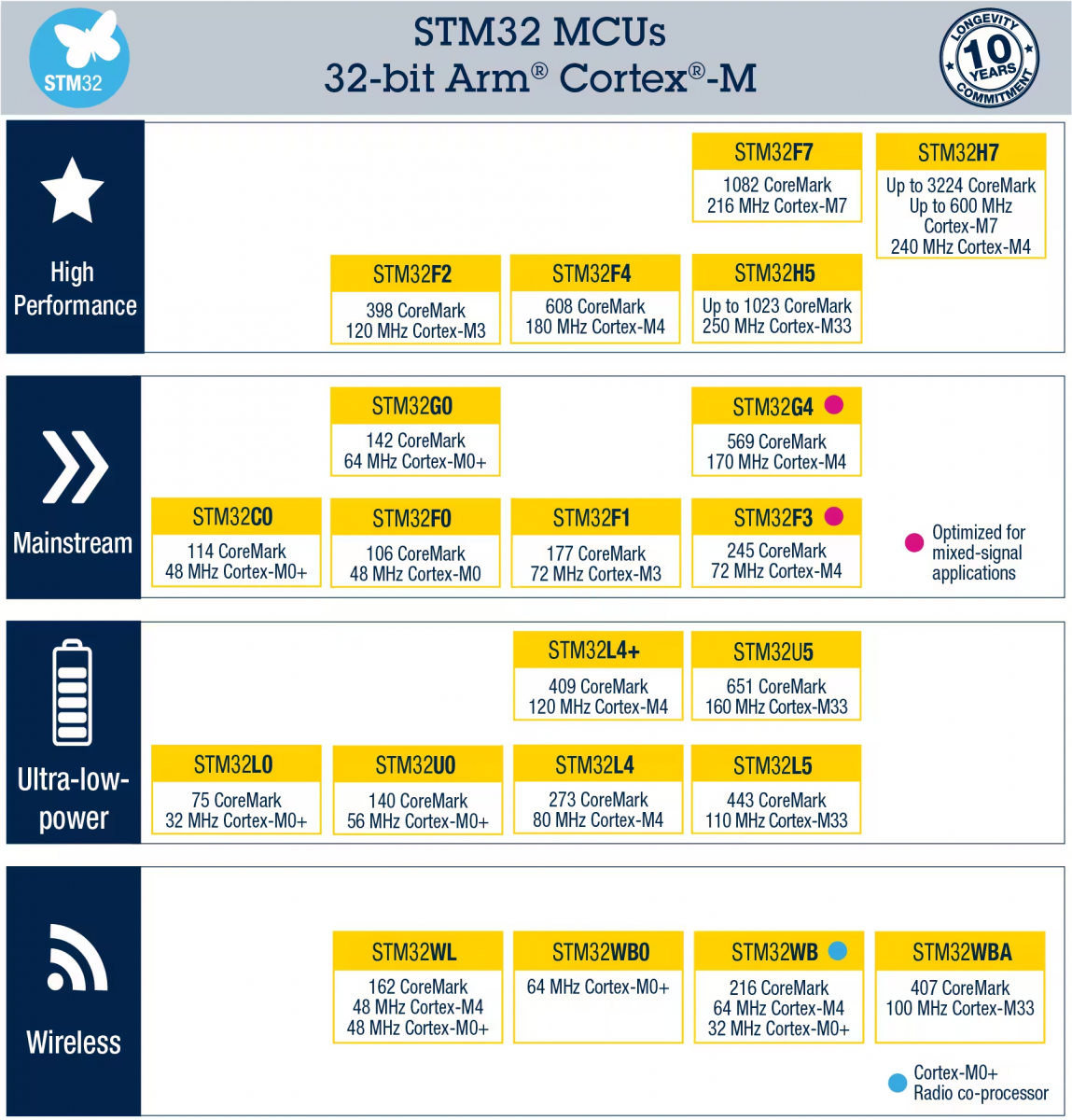
Semiconductors are the foundation of modern electronics. From smartphones and laptops to electric vehicles and solar panels, nearly every piece of technology around us relies on semiconductor materials. But what exactly is a semiconductor, and what function does it perform that makes it so essential in the digital age?
Understanding Semiconductors
A semiconductor is a material that has electrical conductivity between that of a conductor (such as copper or aluminum) and an insulator (such as glass or rubber). In simple terms, semiconductors can conduct electricity under certain conditions but not under others. This unique property allows them to control and regulate the flow of electric current in electronic devices.
The most commonly used semiconductor material is silicon, though others like gallium arsenide and germanium are also widely applied in specific technologies.
The Core Function of Semiconductors
The primary function of a semiconductor is to control electrical current. Unlike metals, which always conduct, or insulators, which do not conduct at all, semiconductors can be engineered to switch between conducting and insulating states. This ability makes them the perfect building blocks for creating electronic components such as diodes, transistors, and integrated circuits.
In essence, semiconductors serve four fundamental functions in electronics:
Switching – Acting as an on/off gate to control the flow of current. This function is vital in digital circuits where binary states (1 and 0) define computation.
Amplification – Increasing the strength of weak electrical signals, as seen in audio devices and communication equipment.
Energy Conversion – Converting energy from one form to another, such as turning sunlight into electricity in solar cells or rectifying alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC) in power supplies.
Signal Modulation – Controlling and shaping signals in telecommunications, ensuring data can be transmitted reliably over long distances.
Without semiconductors, modern computing, telecommunications, and renewable energy systems would not be possible.
Applications in Everyday Life
Semiconductors are embedded in nearly every device we use today. A few notable applications include:
Computers and Smartphones: Microprocessors and memory chips are made entirely of semiconductor components.
Consumer Electronics: Televisions, game consoles, and audio systems all rely on semiconductor chips.
Automotive Industry: Electric vehicles, engine control units, sensors, and safety systems use semiconductors to ensure efficiency and reliability.
Energy Systems: Photovoltaic cells in solar panels use semiconductors to convert sunlight into usable electricity.
Medical Devices: Advanced diagnostic machines, imaging systems, and portable health monitors depend on precise semiconductor chips.
This wide range of applications shows how semiconductors are not just a technical material, but a critical enabler of modern life.
The Role of Transistors and Integrated Circuits
One of the most revolutionary uses of semiconductors is in the creation of the transistor, a device that can switch or amplify signals. Transistors replaced bulky vacuum tubes in the mid-20th century, leading to smaller, faster, and more reliable electronics.
Integrated circuits (ICs), which contain millions or even billions of transistors on a single chip, are the backbone of modern computing and digital systems. Without semiconductors, innovations like artificial intelligence, 5G networks, and cloud computing would simply not exist.
Future of Semiconductors
As technology advances, semiconductors are expected to play an even greater role. Key trends include:
Miniaturization: Chips with smaller transistors for faster and more efficient computing.
Energy Efficiency: Semiconductors designed for lower power consumption in mobile and IoT devices.
New Materials: Beyond silicon, materials like graphene and gallium nitride are being explored for next-generation electronics.
AI and Quantum Computing: Semiconductors will remain essential as the world pushes into new frontiers of computing power.
Conclusion
The function of a semiconductor goes far beyond simple conductivity. By enabling switching, amplification, energy conversion, and signal modulation, semiconductors form the heart of all modern technology. From powering smartphones to driving renewable energy solutions, their role is both irreplaceable and ever-expanding.
Ample Chip Semiconductor Wholesale Supplier
If you are looking for reliable semiconductor products, Ample Chip is a trusted wholesale supplier and partner. The company provides a wide range of semiconductor components, including ICs, transistors, diodes, and memory chips, ensuring stable quality and competitive pricing. With a strong global supply chain and professional technical support, Ample Chip helps businesses secure the components they need for innovation and production. Whether you are in consumer electronics, automotive, industrial, or medical sectors, Ample Chip offers tailored solutions to meet your semiconductor requirements.
Related News
What is a Discrete Semiconductor?
What Are the Uses of Discrete Semiconductors?
What Is the Difference Between Discrete Semiconductors and Module Semiconductors?
How Ample Chip Ensures Authenticity in Semiconductor Procurement