By 2025, ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) has become a core requirement for e-procurement. The EU's CSRD (Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive) is fully in effect, requiring large companies (including supply chain partners) to disclose Scope 3 emissions and social impacts; REACH/RoHS regulations impose stricter restrictions on hazardous substances; and global investors and customers (such as automotive/consumer electronics brands) prioritize ESG-compliant suppliers. Ignoring ESG can lead to lost contracts, fines, or reputational damage.
This article, an original guide from supply chain experts at AMPLE CHIP LIMITED, helps engineers and OEM/ODM procurement personnel achieve compliant procurement. Through practices such as reusing surplus inventory, you can reduce costs by 20-50%, decrease carbon emissions, and improve your company's ESG score.
Above: Sustainable Procurement Framework (Environmental, Social, and Governance Pillars)
Above: Sustainable supply chain management model

Above: Challenges and Opportunities of Green Supply Chains
1. Core Regulations for ESG Compliant Sourcing (Updated 2025)
EU CSRD: From 2025, large companies must report ESG data (including Scope 3 emissions) across their supply chains. Key areas for the electronics industry: Hazardous substance use, waste management, and social responsibility.
REACH/RoHS Extension: New restricted substances added in 2025; full transparency and traceability required across the supply chain.
CSDDD (Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive): Requires assessment of supplier labor/environmental risks; non-EU companies supplying the EU market are also affected.
US SEC Climate Disclosure: Similar requirements to Scope 3, impacting the global supply chain.
Others: TCO Certified (Sustainable Electronics Certification), Conflict Minerals Reporting.
Compliance Tip: Prioritize suppliers with RoHS/REACH certifications to avoid fines.
2. Environmental (E) Dimension: Reducing Carbon Footprint and E-waste
Carbon emissions from the electronics supply chain primarily come from new component production (Scope 3, up to 80%). Reusing surplus inventory can significantly reduce the impact.
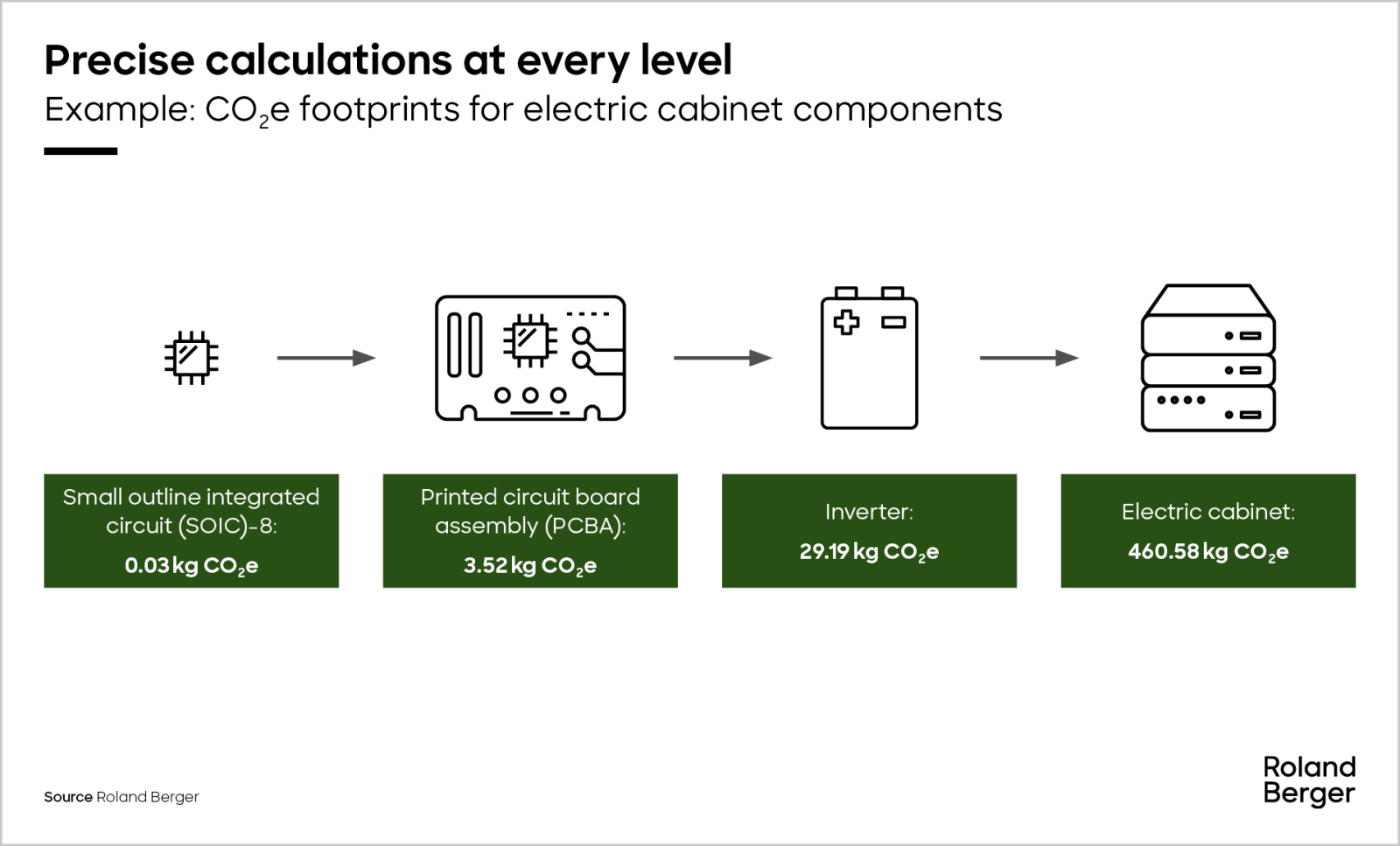
Above: Example of product carbon footprint calculation
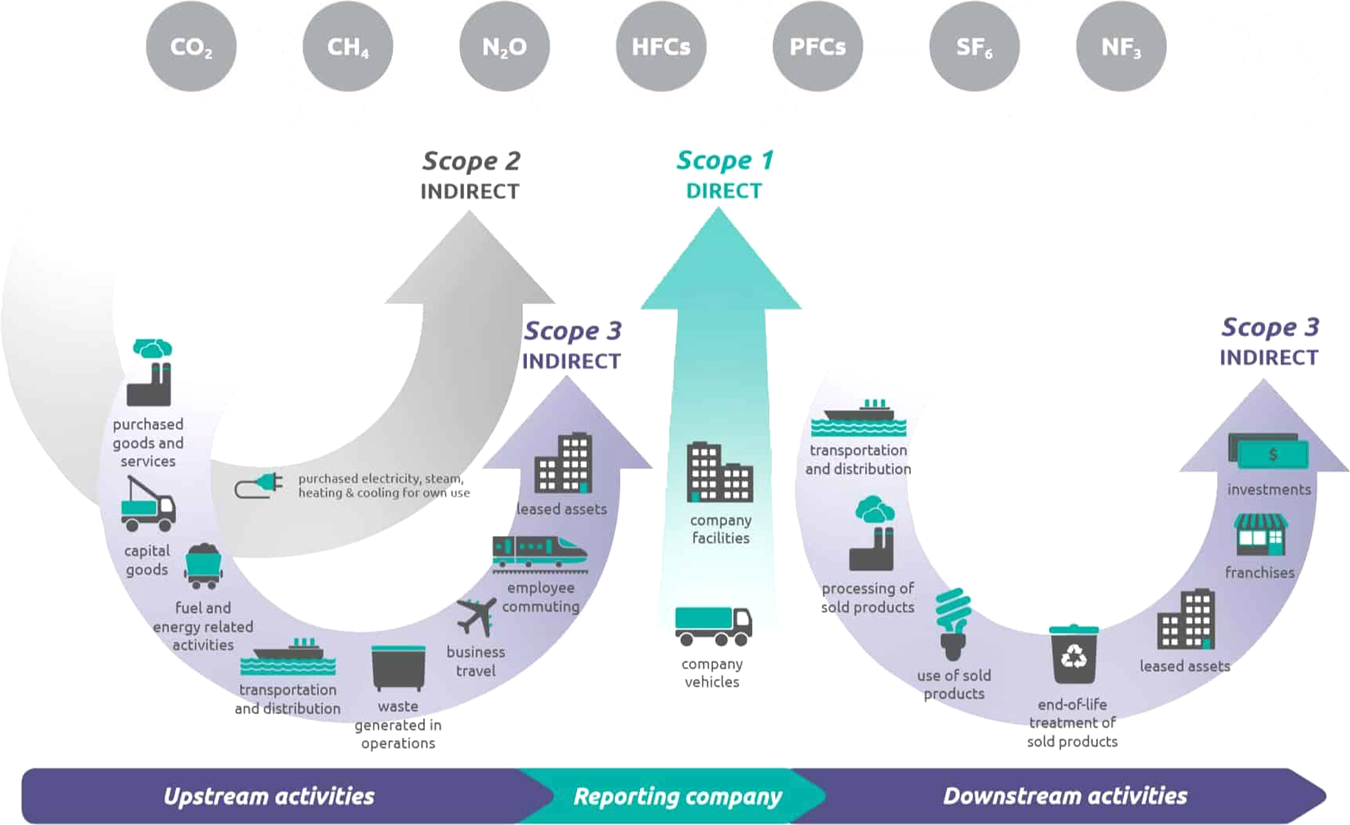
Above: Supply Chain Scope 3 Emissions Data Sharing Model
Practical steps:
- Calculate BOM carbon footprint: Use tools to estimate emissions from new parts vs. remaining inventory (reuse can reduce emissions by 70-90%).
- Prioritize surplus inventory: new, unused parts to avoid energy consumption in new production.
- Circular economy: Choose recyclable packaging and avoid harmful substances.
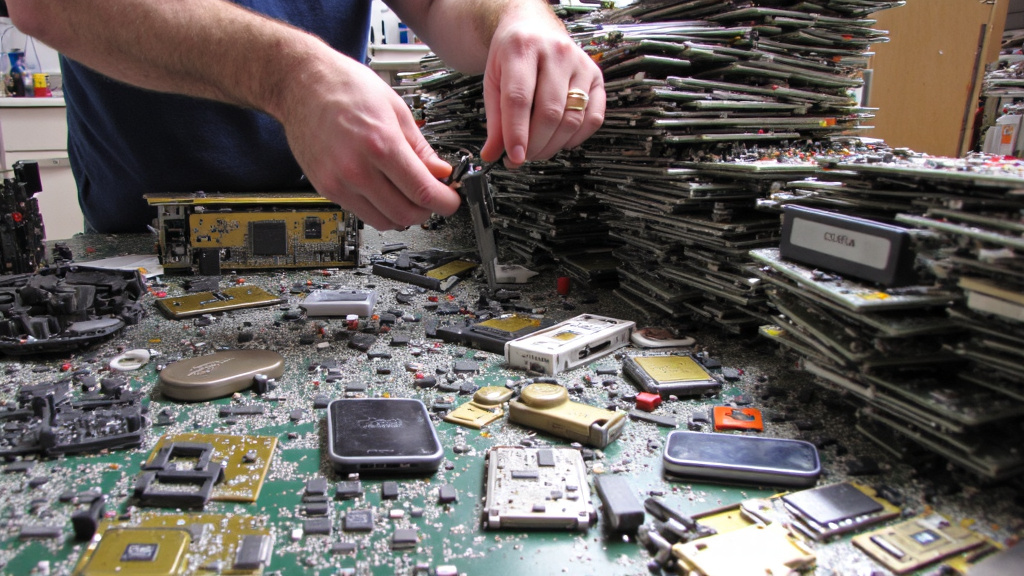

Above: Electronic waste recycling process (circuit board reuse)

Above: Example of component recycling and reuse
Benefits: Every ton of recycled parts can reduce emissions equivalent to planting 10 trees.
3. Social (S) Dimension: Ethical Supply Chains and Labor Responsibility
- Key points: Avoid conflict minerals and forced labor.
- Practices: Require suppliers to provide labor audit reports; prioritize local/transparent supply chains.
- 2025 Trend: Customers are requiring suppliers to conduct ESG assessments (such as EcoVadis ratings).
4. Governance (G) Dimension: Transparency and Risk Management
- Practice: Establish supplier codes, conduct regular audits, and share data transparently.
- Tool: The BOM upload platform automatically checks for compliance labels.
5. Practical Cases and Implementation Steps
- Case Study: A car OEM purchased MCUs from its surplus inventory, which will reduce CO2 emissions by 40 tons and lower costs by 25% by 2025, in compliance with the CSRD report.
- 7-Step Implementation Guide:
- Assess current supply chain ESG risks.
- Policy formulation: Prioritize surplus inventory + green certification.
- Tool integration: BOM matching platform (such as AMPLE CHIP).
- Supplier collaboration: sharing data and joint auditing.
- Calculation indicators: carbon footprint, waste reduction.
- Report preparation: Compliant with CSRD/ESRS standards.
- Continuous optimization: Annual audit.
Conclusions and Calls to Action
By 2025, ESG compliant sourcing will not only be a regulatory requirement but also a competitive advantage. Through the reuse of surplus inventory, you can achieve cost savings, risk reduction, and sustainability goals.
Take action now: Upload your BOM to AMPLE CHIP to get an AI-matched compliant surplus inventory quote and view a personalized sustainability report. Contact us for a free ESG assessment consultation!